accumulated earnings tax calculation
The accumulated earnings tax AET is a penalty tax imposed on corporations for unreasonably accumulating earnings in the corporation. 531 and 532.

What Are Retained Earnings How To Calculate Retained Earnings Mageplaza
The Accumulated Earnings Tax is more like a penalty since it is assessed by the IRS often years after the income tax return was filed.
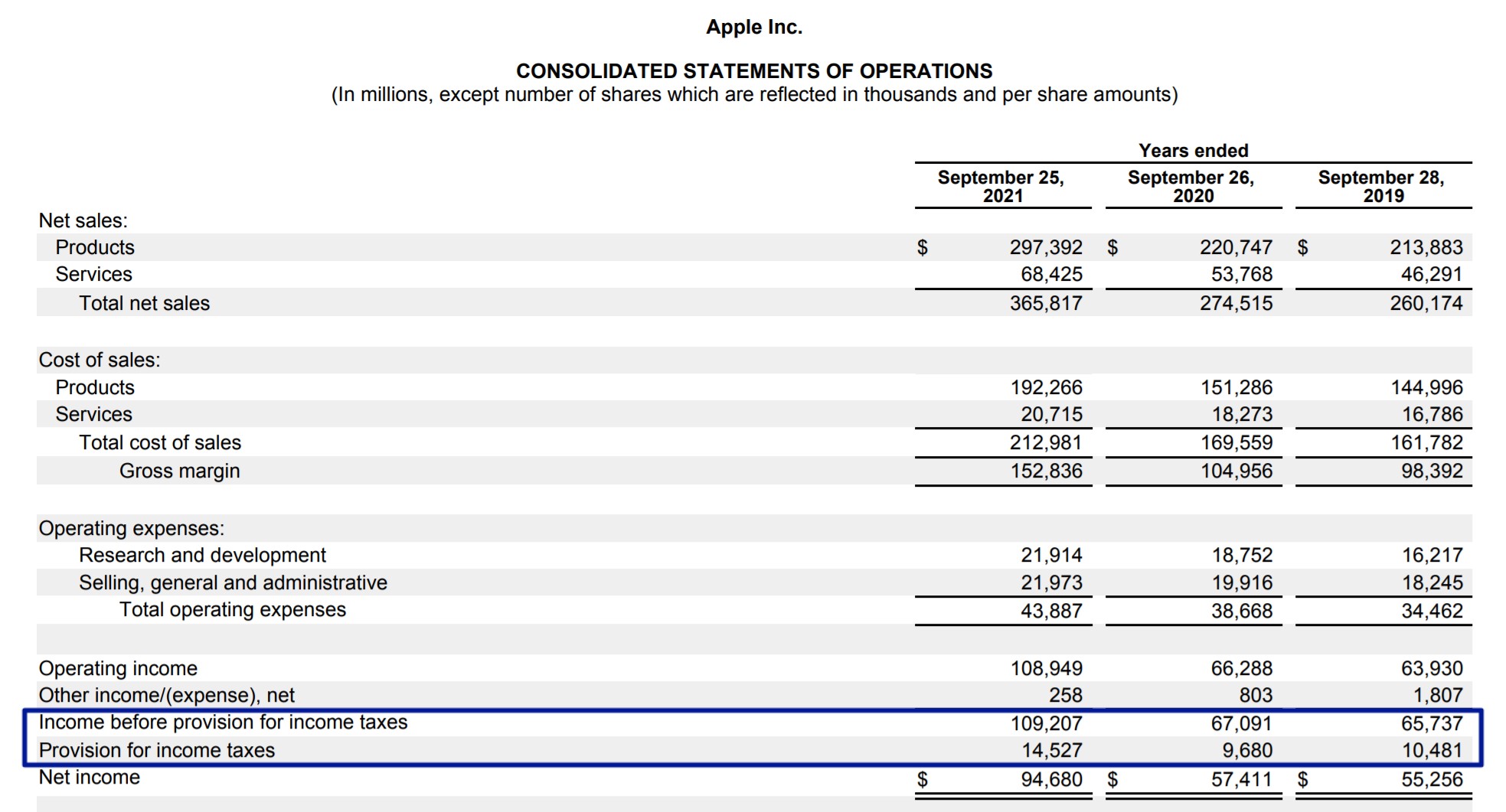
. 1000000 - EP depreciation 500000 - Federal income taxes paid 1500000 - Interest paid but not deducted 2500000 - 50 of meals. Accumulated earnings and profits E P is an accounting term applicable to stockholders of corporations. This amount is recorded in the financial statement at the end of the year as deferred income.
Calculation of EP. This template calculates the accumulated earnings tax. 22500000 Tax depreciation.
Calculation of Accumulated Retained Earnings. Accumulated earnings and profits are a companys net profits after paying dividends to. IRC Section 535c1 provides that.
The Accumulated Earnings Tax is computed by multiplying the Accumulated Taxable Income IRC Section 535 by 20. The Accumulated Earnings Tax is computed by multiplying the Accumulated Taxable Income IRC Section 535 by 20. The accumulated earnings tax is imposed on the accumulated taxable income of every corporation formed or availed of for the purpose of avoiding the income tax with respect to its shareholders by permitting earnings and profits to accumulate instead of being divided or distributed.
In deciding whether the penalty tax should be im-posed the key question is whether the corporation was in the language of section 532 formed or availed of for the purpose of avoiding the income tax with respect. The tax is assessed at the highest individual tax rate on the corporations accumulated income and is in addition to the regular corporate income tax. The remaining 283000 distribution amount will be absorbed by the accumulated EP balance of.
The accumulated earnings tax is a 20 tax that will be applied to C corporations taxable income. The accumulated earnings tax is equal to 20 of the accumulated taxable income and is imposed in addition to other taxes required under the Internal Revenue Code. In periods where corporate tax rates were significantly lower than individual tax rates an obvious incentive existed for.
A corporation may be allowed an accumulated earnings credit in the na-ture of a deduction in computing accu-mulated taxable income to the extent it. Accrued means tax actually payable based on reported income not tax based on income a corporation would include if it reported all items of income and deductions under the accrual method. The tax is in addition to the regular corporate income tax and is assessed by the IRS typically during an IRS audit.
To calculate the number of accumulated earnings the sum of the accumulated profits at the beginning of the year must be added to the current accumulated earnings less any dividends given to investors. The result is 0625. The regular corporate income tax.
How Does Accumulated Earnings Tax Work. Divide the current year earnings and profits 10000 by the total amount of distributions made during the year 16000. The accumulated earnings tax also called the accumulated profits tax is a tax on abnormally high.
Of the 400000 distribution the current-year EP will cover the first 117000. If a C corporation retains earnings doesnt distribute them to shareholders above a certain amount an amount which the IRS concludes is beyond the reasonable needs of the business the corporation may be assessed tax penalty called the accumulated earnings tax IRC section 531 equal to 20 percent 15 prior to 2013 of accumulated taxable income. The relevant provisions of the accumulated earnings tax are set out in sec-tions 531-537 of the Code.
The accumulated earnings tax is a charge levied on a companys retained earnings. The tax rate on accumulated earnings is 20 the maximum rate at which they would be taxed if distributed. The profit brought forward will be 100000 700000 - 300000 500000.
A 400000 distribution in year 6 will be sourced first from the current-year EP as shown in Exhibit 3. 25000 250000 Accumulated EP at. The accumulated earnings tax will take effect if a firm decides to keep its profits or earnings instead of distributing dividends to.
A company must be careful to justify the amount of its accumulated retained earnings since some governments tax an excessive amount of these accumulated earnings on the grounds that they should have been distributed to shareholders who would then have been taxed for their dividend income. For example lets assume a certain company has 100000 in accumulated. REASONABLE NEEDS OF THE BUSINESS26 USC.
The AET is a penalty tax imposed on corporations for unreasonably accumulating earnings. The tax rate is 20 of accumulated taxable in-come defined as taxable income with adjustments including the subtraction of federal and foreign income taxes. The accumulated earnings tax is considered a penalty tax to those C corporations that have accumulated over 250000 in earnings 150000 for PSC corporations and if that excess amount has not been distributed to shareholders in the form of a dividend.
Multiply each 4000 distribution by the 0625 figured in 1 to get the amount 2500 of each distribution treated as a distribution of current year earnings and profits. The accumulated earnings tax is a 20 penalty that is imposed when a corporation retains earnings beyond the reasonable needs of its business ie instead of paying dividends with the purpose of avoiding shareholder - level tax seeSec. Accrued means tax actually payable based on reported income not tax based on income a corporation would include if it reported all items of income and deductions under the accrual method.
The company pays the. Also called the accumulated profits tax it is applied when tax authorities determine the cash on hand to be an excessively high amount. The company made a net profit of 700000 and paid 300000 in dividends in the same year.
Calculating the Accumulated Earnings RE Initial RE net income dividends. Accumulated Earnings Tax can be reduced by reducing Accumulated Taxable Income. The tax is assessed by the IRS rather.
The purpose of the accumulated earnings tax is to compel. Therefore in computing its accrued tax Metro would include only the current years reported installment income. When the net profits of a company increase the accumulated earnings also increase.

Retained Earnings Formula And Excel Calculator

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study

Determining The Taxability Of S Corporation Distributions Part Ii
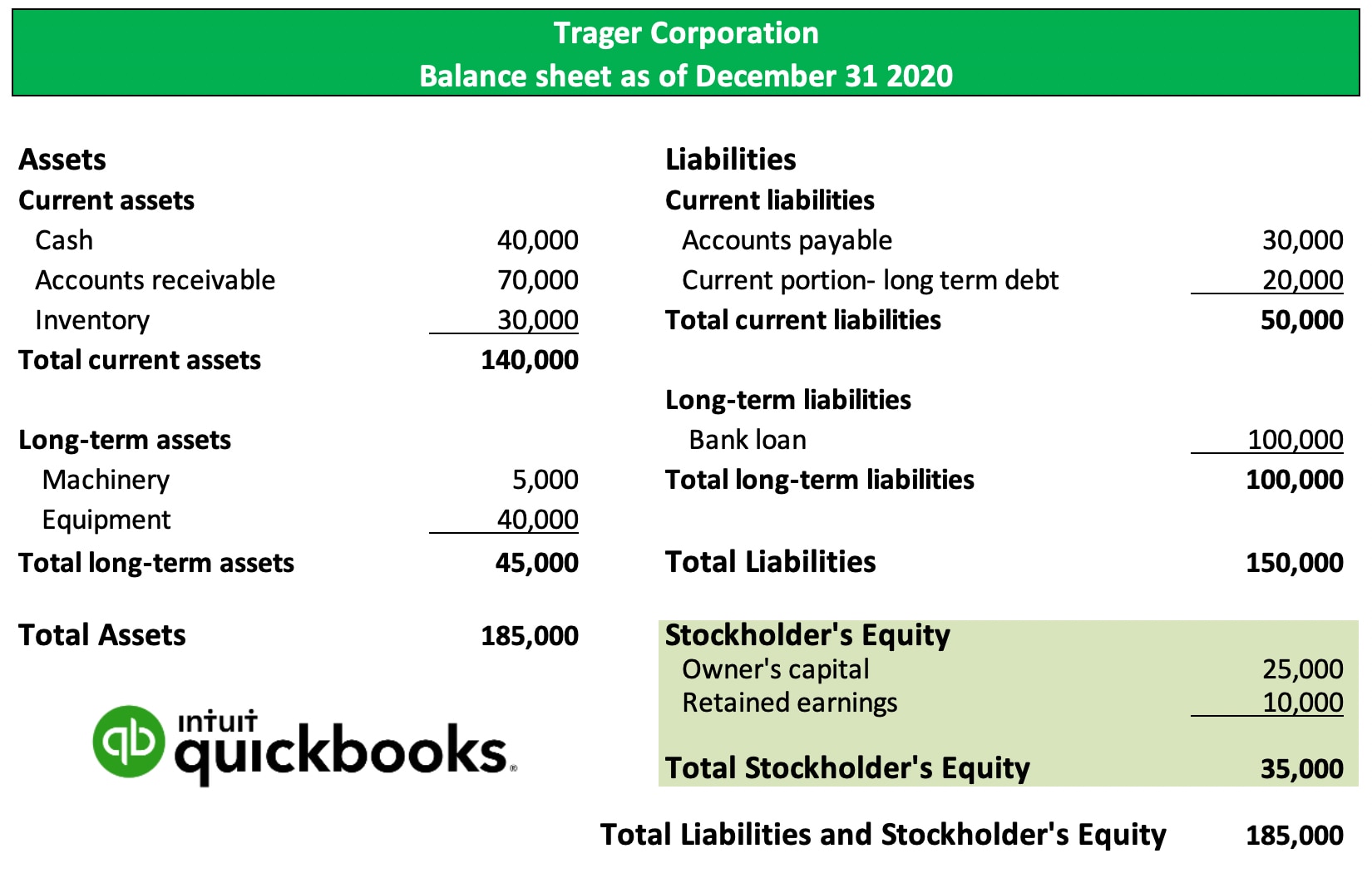
What Are Retained Earnings Quickbooks Canada
Sale Of Stock Of A Cfc Example Of The Potential Benefit Of Code 1248 B International Tax Blog
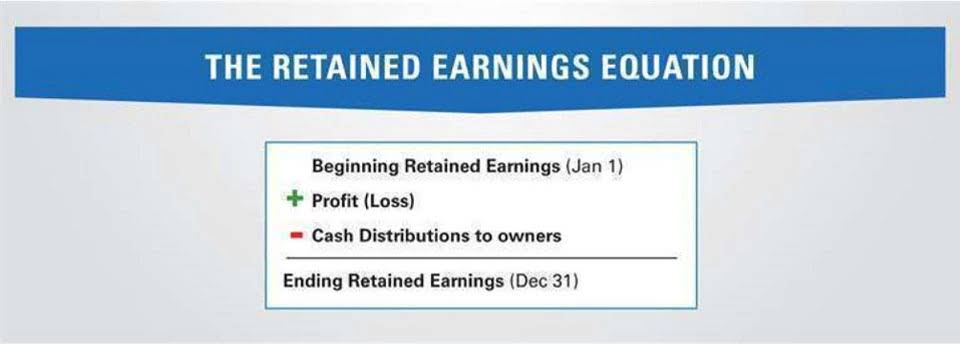
What Are Retained Earnings Definition And Explanation Bookstime

Understanding The Accumulated Earnings Tax Before Switching To A C Corporation In 2019

Accumulated Deficit Definition And Causes Of Negative Retained Earnings
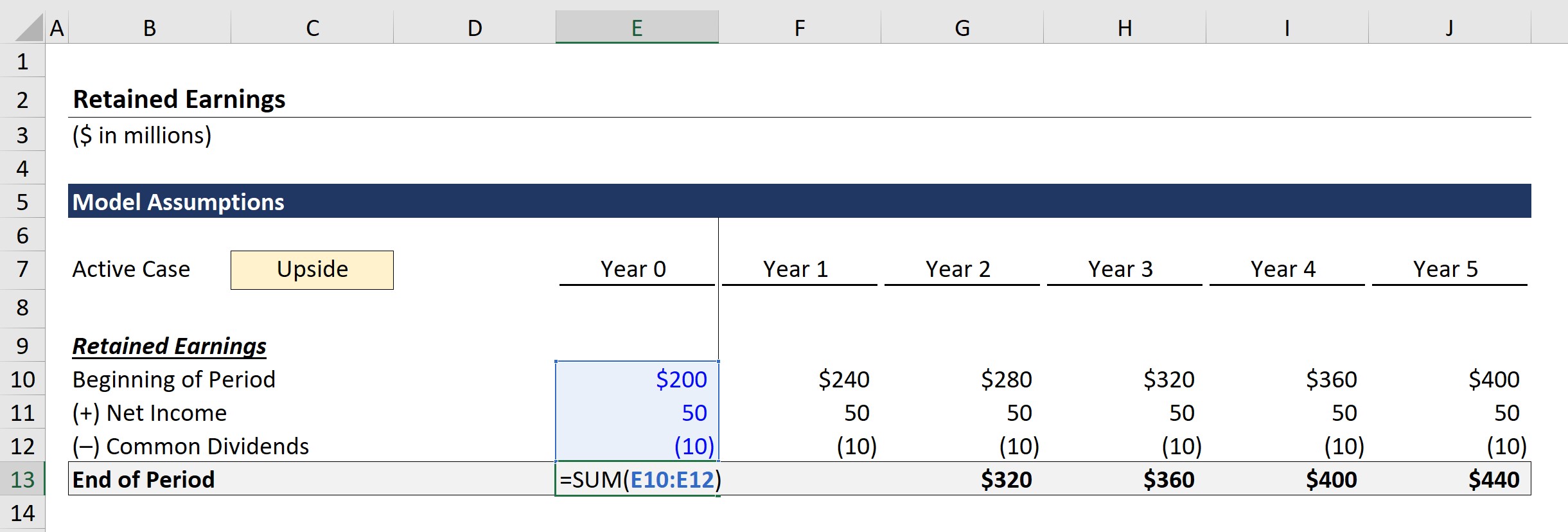
Retained Earnings Formula And Excel Calculator

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

Determining The Taxability Of S Corporation Distributions Part I

Effective Tax Rate Formula And Calculation Example
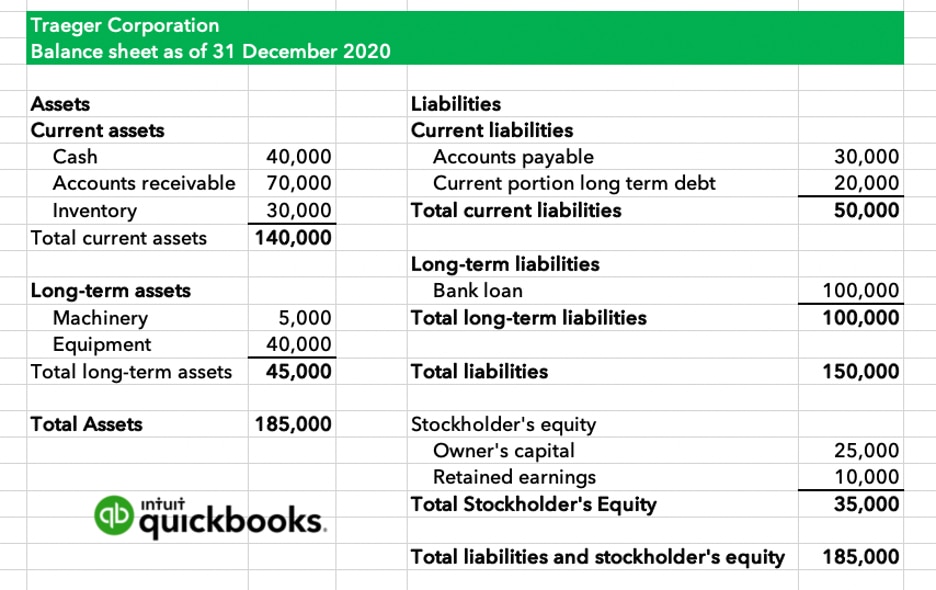
What Are Retained Earnings Quickbooks Australia

Everything You Need To Know About Retained Earnings Bookstime
